Querying SQL Server For A List of Tables
[SQL Server]
In our previous post, we looked at Querying SQL Server For A List of Stored Functions.
In this post, we will look at how to query SQL Server for a list of tables.
There are three ways to achieve this:
sys.tablessystem view- INFORMATION_SCHEMA
sys.objectssystem viewsp_tablesprocedure
sys.tables
SQL Server exposes a system view, sys.tables, that you can query for all the tables in the active database.
select * from sys.tables
This will return the following:
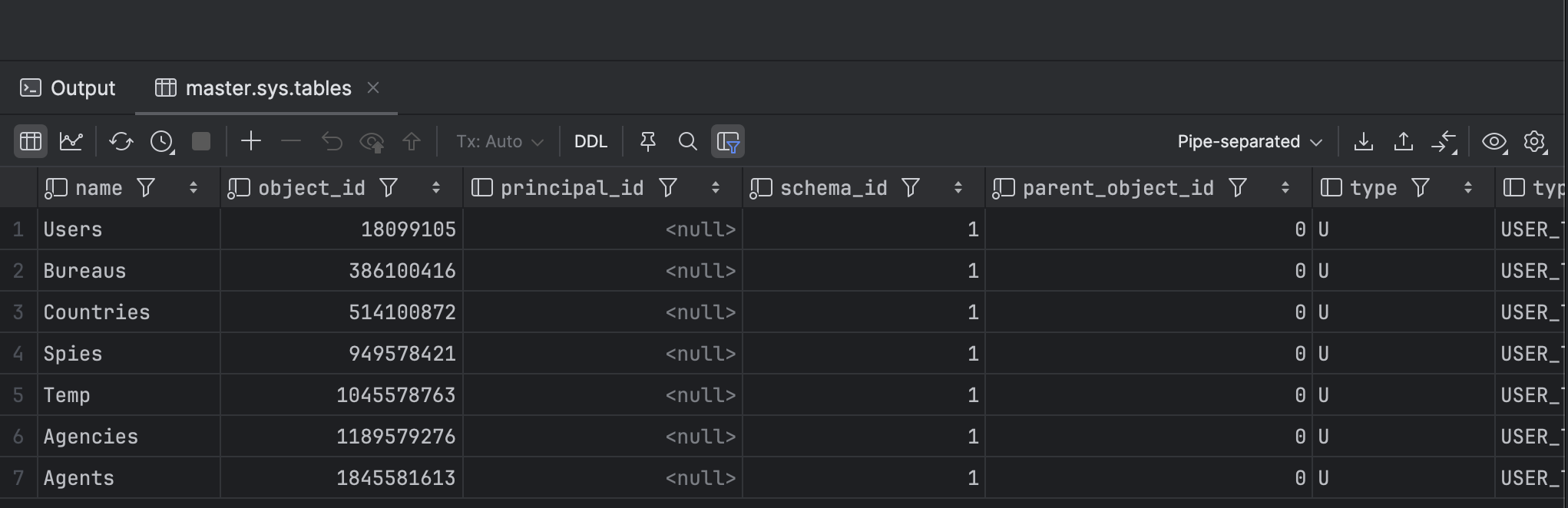
The full list of columns is as follows:
select name,
object_id,
principal_id,
schema_id,
parent_object_id,
type,
type_desc,
create_date,
modify_date,
is_ms_shipped,
is_published,
is_schema_published,
lob_data_space_id,
filestream_data_space_id,
max_column_id_used,
lock_on_bulk_load,
uses_ansi_nulls,
is_replicated,
has_replication_filter,
is_merge_published,
is_sync_tran_subscribed,
has_unchecked_assembly_data,
text_in_row_limit,
large_value_types_out_of_row,
is_tracked_by_cdc,
lock_escalation,
lock_escalation_desc,
is_filetable,
is_memory_optimized,
durability,
durability_desc,
temporal_type,
temporal_type_desc,
history_table_id,
is_remote_data_archive_enabled,
is_external,
history_retention_period,
history_retention_period_unit,
history_retention_period_unit_desc,
is_node,
is_edge,
data_retention_period,
data_retention_period_unit,
data_retention_period_unit_desc,
ledger_type,
ledger_type_desc,
ledger_view_id,
is_dropped_ledger_table
from sys.tables
The columns you will most likely use are these:
select name,
create_date,
modify_date
from sys.tables
This technique, however, will not return temporary tables.
INFORMATION_SCHEMA
You can also use the INFORMATION_SCHEMA system view, filtering as follows:
SELECT *
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES
WHERE TABLE_TYPE = 'BASE TABLE'
ORDER BY TABLE_SCHEMA, TABLE_NAME;
This will return the following:
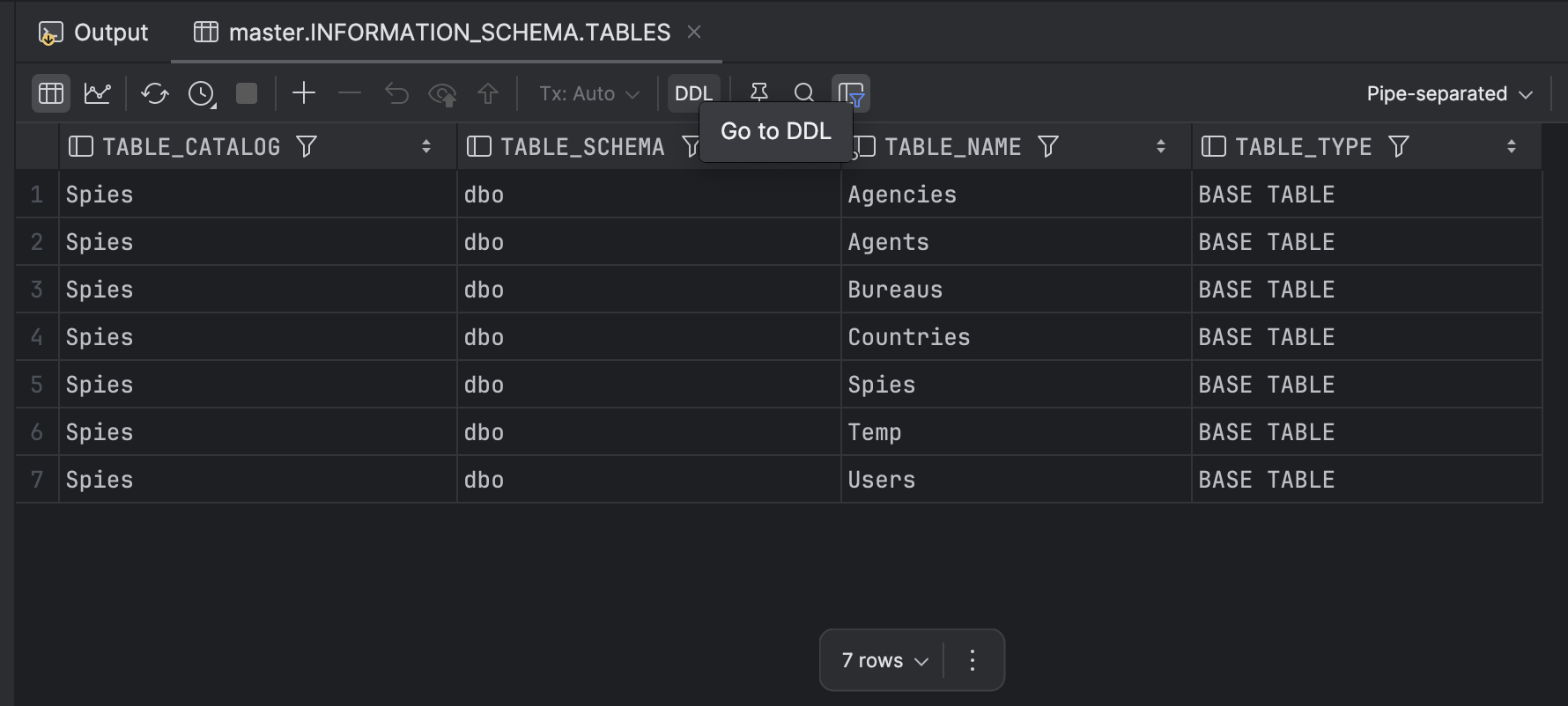
The columns returned are the following:
SELECT TABLE_CATALOG,
TABLE_SCHEMA,
TABLE_NAME,
TABLE_TYPE
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES
WHERE TABLE_TYPE = 'BASE TABLE'
ORDER BY TABLE_SCHEMA, TABLE_NAME;
This technique will not return temporary tables either.
sys.objects
SQL Server exposes a system view, sys.objects, that you can use to query for tables.
You can query it as follows:
SELECT *
FROM sys.objects
WHERE type = 'U' --User tables
ORDER BY name;
This will return the following:
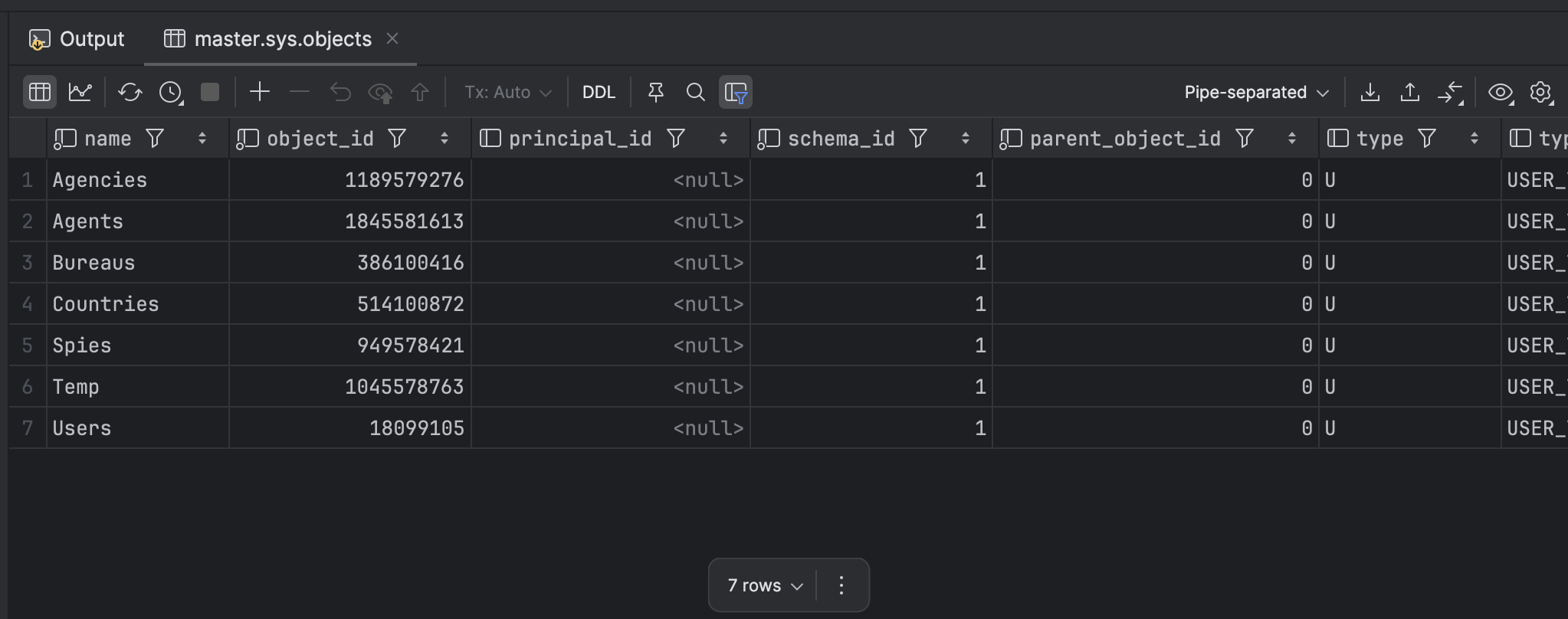
The columns returned are as follows:
SELECT name,
object_id,
principal_id,
schema_id,
parent_object_id,
type,
type_desc,
create_date,
modify_date,
is_ms_shipped,
is_published,
is_schema_published
FROM sys.objects
WHERE type = 'U' --User tables
ORDER BY name;
To include views, update the filter as follows:
SELECT *
FROM sys.objects
WHERE type in ('U','V')
ORDER BY name;
This will return the following:
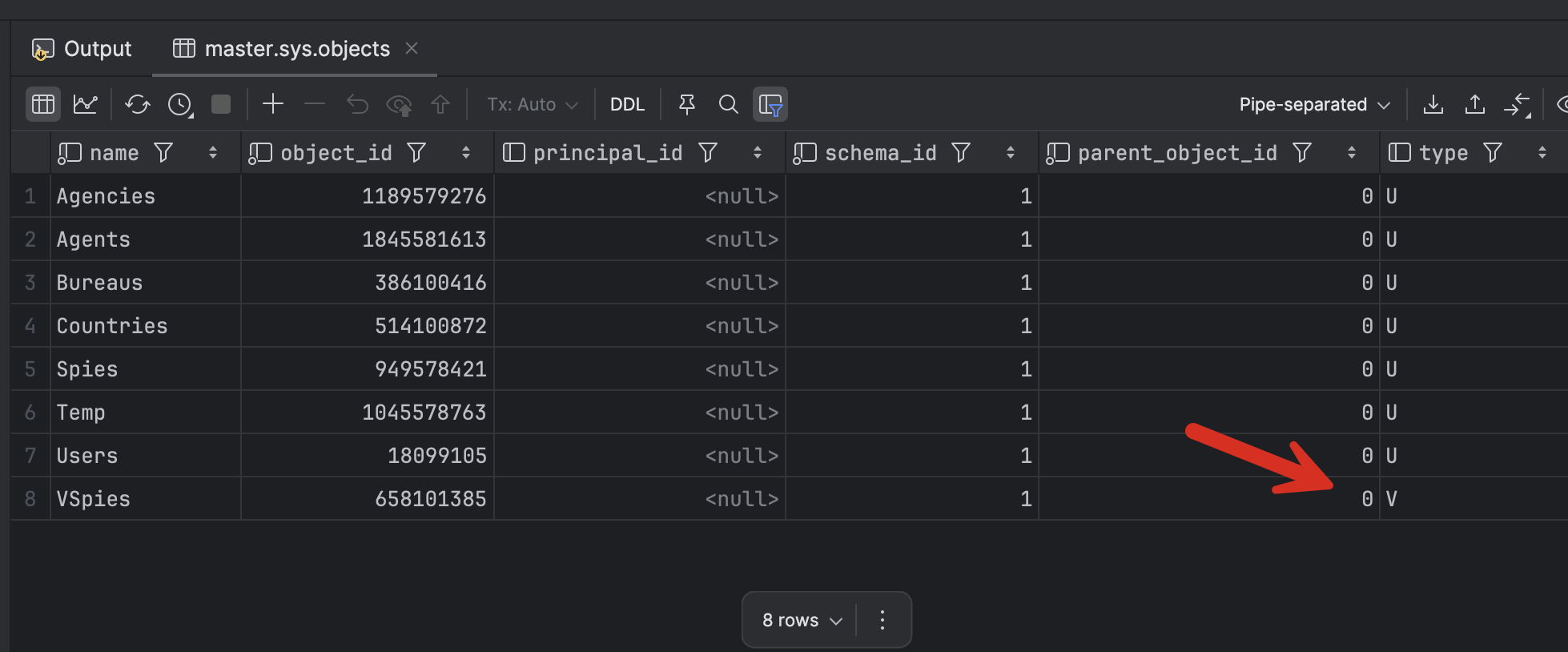
sp_tables
SQL Server exposes a system stored procedure, sp_tables.
It takes four parameters:
table_name- The name of the table used to return catalog information. If not provided,nullis passed.table_owner- The schema to which the table belongs. If not provided,nullis passed.table_qualifier- The name of the table qualifier. Typically, the database name. Defaults tonullfUsePattern- Determines whether the underscore (_), percent (%), or brackets ([and]) are interpreted as wildcard characters. Defaults to1
To get a usable result, pass at least the owner
sp_tables null,'dbo'
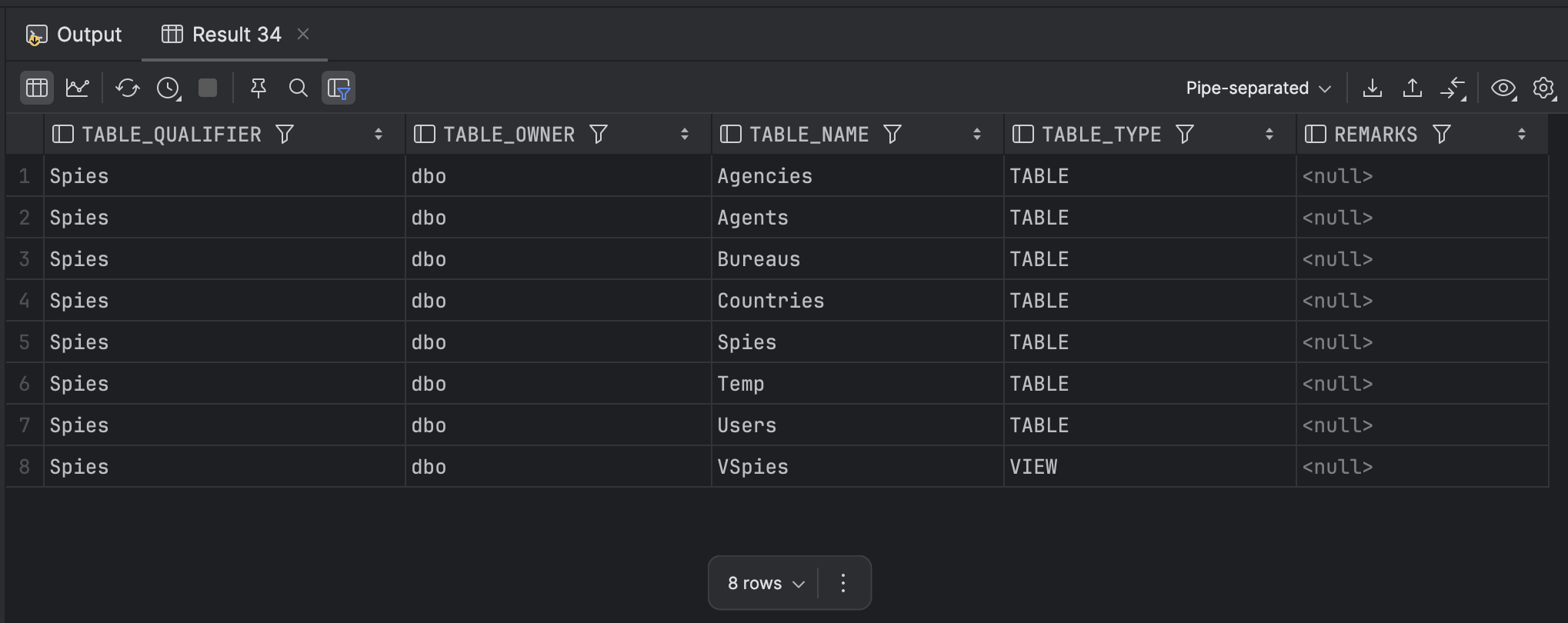
This procedure will return views as well as tables.
If you call the procedure without any parameters, you will get the following result:
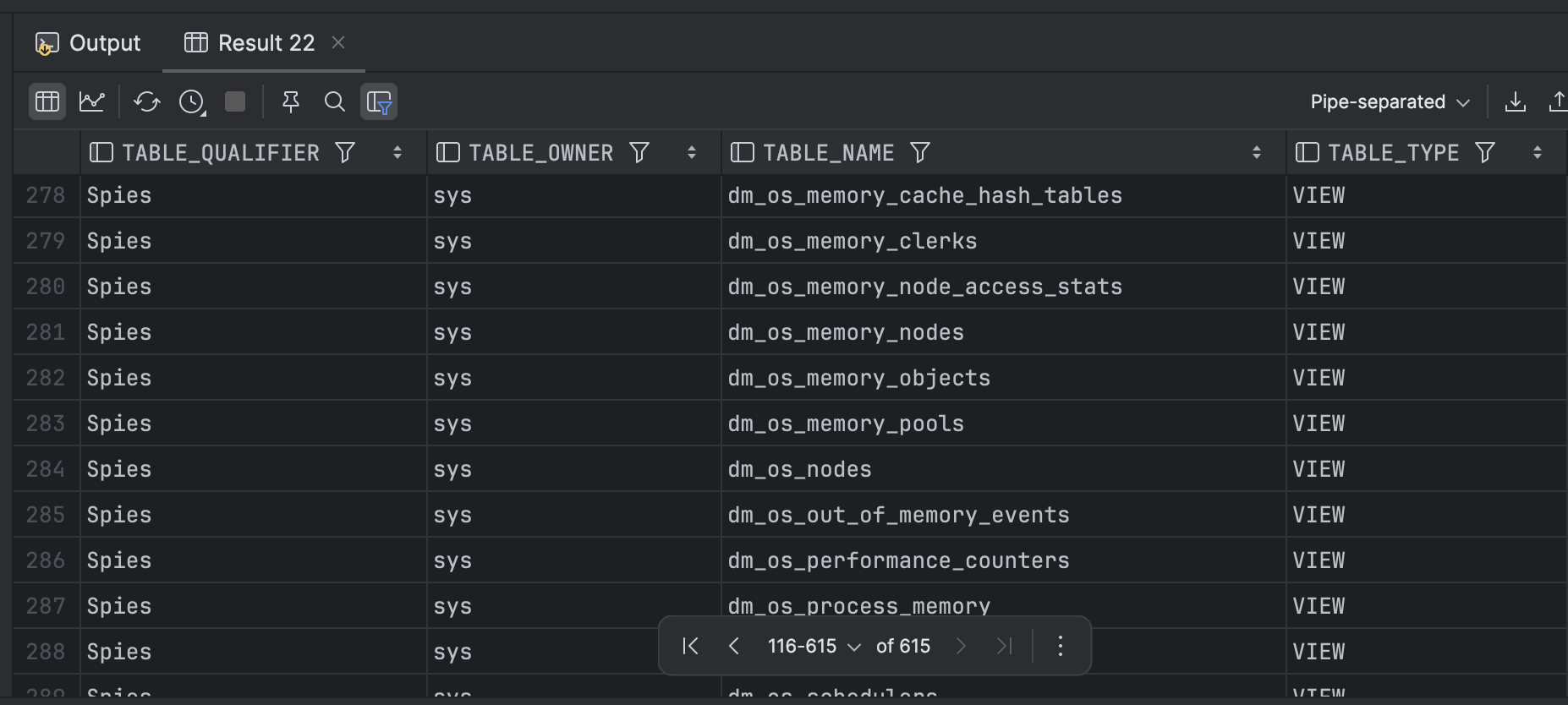
This is because it will also return a variety of system tables and views.
TLDR
SQL Server offers four ways to query for a list of tables.
Happy hacking!